The 922 MHz frequency lies within the 900 MHz UHF band, which is widely used for low-power communications across industrial, scientific, medical (ISM), and IoT applications. While not globally harmonized, the 922 MHz band is especially important in Asia-Pacific and South America, with varying allocations in different ITU regions.
🌍 Frequency Summary
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Center Frequency | 922 MHz |
| Common Range | 902–928 MHz (ITU Region 2), 915–928 MHz (Region 3) |
| ITU Regions | 🌍 Region 1 (partial), 🌎 Region 2, 🌏 Region 3 |
| License Type | Mostly license-exempt (varies by country) |
| Primary Use | RFID, LPWAN (e.g., LoRa), industrial telemetry |
| Global Harmonization | Partial (region-specific ISM bands) |
🔌 What Is 922 MHz Used For?
922 MHz is used for a variety of short-range and low-power wireless systems, including:
- RFID (UHF) tags and readers for logistics and retail
- LoRaWAN (LPWAN) networks for smart agriculture, metering, and IoT sensors
- Wireless M-Bus in utilities
- Telemetry in industrial and infrastructure applications
- Home automation systems in specific regions
It is favored for its propagation characteristics—being less prone to attenuation compared to higher frequency ISM bands like 2.4 GHz.
🌐 Regional Use Overview
| Region | Typical Allocation for 922 MHz |
|---|---|
| 🌍 Region 1 (Europe, Africa, Middle East) | Generally not available for ISM use at 922 MHz; instead uses 868 MHz |
| 🌎 Region 2 (Americas) | 902–928 MHz ISM band widely used in the US, Canada, Brazil, etc. |
| 🌏 Region 3 (Asia-Pacific) | Countries like Japan, Singapore, and Malaysia use 920–925 MHz for RFID, IoT |
📻 Technical Characteristics
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Modulation Types | LoRa, GFSK, OOK, ASK, FHSS |
| Typical Bandwidth | 125 kHz to 1 MHz per channel |
| Transmission Power | 10–500 mW depending on country regulations |
| Range (LoRa) | Up to 10–15 km in rural areas |
🔐 License & Restrictions
- Mostly license-free, subject to national power and duty cycle limits.
- Some countries require type approval or conformance to local standards (e.g., ARIB in Japan, FCC in the US).
- Spectrum sharing is common due to unlicensed status—interference management is application-level.
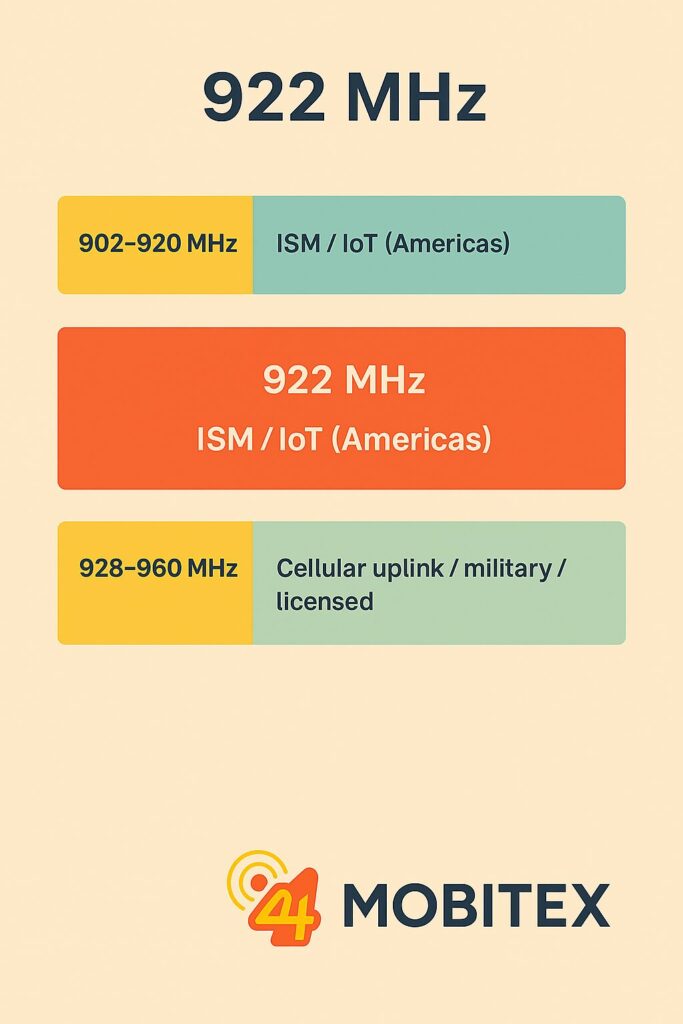
🔍 Adjacent Bands
| Band | Frequency Range | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 902–920 MHz | ISM/IoT (Americas) | LoRa, RFID, smart meters |
| 920–928 MHz | ISM/IoT (Asia-Pacific) | RFID, LoRa, SRD |
| 928–960 MHz | Cellular uplink, military, licensed | LTE Band 8 uplink, legacy systems |
🛠️ Related Technologies
- LoRaWAN (operates between 902–928 MHz depending on region)
- Sigfox (used 920–922 MHz in Asia before network exit)
- Zebra and Impinj RFID readers
- LPWAN gateways and asset trackers
🧭 Regulatory Authorities
- FCC (US, Region 2)
- ARIB (Japan)
- ACMA (Australia)
- Anatel (Brazil)
- Ofcom (UK) – Note: 922 MHz not used for ISM
📜 Historical Context
- Adopted in Region 2 as part of the FCC’s original ISM band allocations.
- Gained traction in Japan after 2005 when the 920 MHz band was released for UHF RFID.
- Became a core band for LoRaWAN networks globally.
- Used in COVID-19 response for asset tracking and proximity monitoring.
🧾 Summary
The 922 MHz frequency is a flexible, regional ISM/LPWAN workhorse. It supports applications from retail logistics to smart agriculture, offering long-range, low-power connectivity where 2.4 GHz falls short. Despite fragmented harmonization, it remains one of the most vital sub-GHz frequencies in global wireless communications.