Frequency
136 MHz
Range
118–137 MHz
Band Group
VHF (30–300 MHz)
🌐 Summary
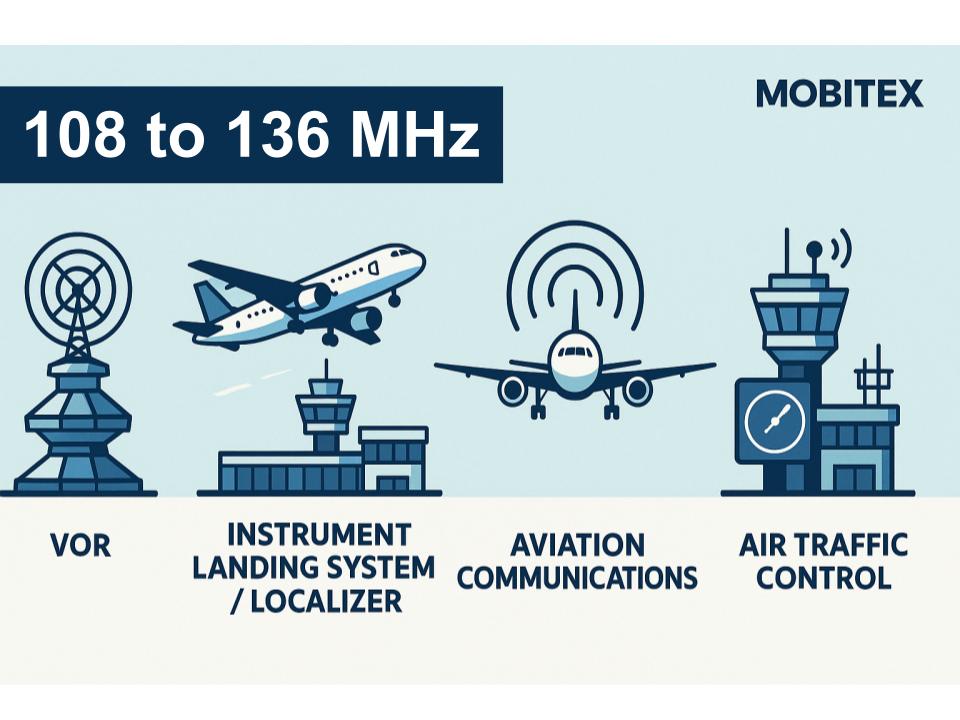
The 136 MHz allocation is part of the VHF (30–300 MHz) spectrum. This range is used worldwide for critical applications that keep our communications and infrastructure running smoothly. On this page we highlight how each band is applied in real systems, from regulatory assignments to everyday devices. Our goal is to make spectrum data clear and practical for engineers, regulators, and enthusiasts alike.
Key uses of this band include: 136 MHz: Air traffic comms; Aircraft radios, ATC comms.
Upper end of civil airband; data links (e.g., ACARS segments) coexist with voice in parts of 136 MHz.
🔍 Explore the full RF Spectrum database
📡 Band & Geometry key
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Wavelength (m) | 2.206 |
| Waveforms | – |
| Antenna Form Factor (Typical) | ¼-wave ≈ 55.1 cm |
| Band Family | Aeronautical |
| Band | Aeronautical mobile (R) (civil airband) |
| Primary Common Name | Aeronautical mobile (R) (civil airband) |
| FSPL @ 1 km [dB] | 75.110778167404 |
| FSPL @ 10 km [dB] | 95.110778167404 |
| Fresnel Radius @ 1 km (m) | 23.482722058869 |
| Band Group | VHF (30–300 MHz) |
| Tax Band Family | VHF |
| Tax Band Class | VHF Airband |
🧩 Applications & Usage
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Primary Application | – |
| Lower Neighbor Use | Aeronautical radionavigation (VOR/ILS) |
| Upper Neighbor Use | Meteorological-satellite / Space operation |
| Typical Services Devices | Air traffic comms |
| Market Common Devices | Aircraft radios, ATC comms |
| Refarming Use | No |
| Device Ecosystem Size | Medium |
| Device Hotspots (MHz) | 136 |
| Device Category | Specialized Industrial / Scientific Equipment |
| Typical Use Cases | – |
| Modulation (Device) | Varies by device |
| Channel Width (Device) [kHz] | Varies |
| Device Region Profiles | Varies by country / allocation |
| Per-Region EIRP Or Duty (Device) | Varies by regulation |
| Allocation Relevance (Device) | Medium |
| Adjacent-Band Collision Risks (Device) | Low–Moderate |
| Example Devices Or Skus | Specialized Industrial / Scientific Equipment |
| Common Protocols | VHF AM Voice (8.33 kHz); VDL Mode 2 (select freqs) |
🗒️ Notes
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Receiver Selectivity Notes | ≥60 dB @ ±8.33 kHz |
| Interference Notes | Critical safety communications |
| Compatibility Risk Notes | Aviation-critical service nearby/in-band; In sensitive band: Aeronautical VHF (Airband) |
| Notes | Upper end of civil airband; data links (e.g., ACARS segments) coexist with voice in parts of 136 MHz. |
| Propagation Notes | Strong coverage, good indoor penetration |
⚙️ Technical Rules
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Lower Band Frequency Limit | 118 |
| Upper Band Frequency Limit | 137 |
| EIRP Indoor Limits | Licensed only |
| EIRP Outdoor Limits | Licensed only |
| PSD Limit | — |
| Emission Mask Class | Airband AM 8.33 kHz |
| Guardband Minimum [kHz] | 8.33 |
| Typical Bandwidths | 6–8 kHz |
| Autocalculated Bandlimits | No |
| Typical Bandwidths (Estimated) | 6–8 kHz |
| Max EIRP [dBm] | Varies by regulation |
| Power Source Or Duty Profile (Typical) | – |
| Channelization Plan | – |
| Channelization | – |
| Guard Band Requirement | – |
| OOB Emission Limit [dBm/MHz] | -13 (baseline) |
| Spurious Emission Limit (dBm) | -30 (baseline) |
| RX Blocking Min [dBm] | -15 (planning) |
| Duplexing | Half-duplex |
| Duplexing Information | Simplex (AM voice) |
| Uplink Pairing | – |
| Downlink Pairing | – |
| Paired Band Info | – |
| Max EIRP [dBm] | – |
| Channelization Block Size | 25 kHz or 8.33 kHz spacing |
| 3GPP Band Number | |
| Example 3GPP Bands | – |
| LTE Uplink Bands | – |
| LTE Downlink Bands | – |
| NR Uplink Bands | – |
| NR Downlink Bands | – |
| Guard Bands | – |
| Protocol Or Standard | – |
🌎 Country Overrides
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Tax Service Category | Other / Various |
| Tax License Type | Safety-of-Life |
| Tax Regions | Global / Varies |
| ITU Region 1 | Aeronautical mobile (R) |
| ITU Region 2 | Aeronautical mobile (R) |
| ITU Region 3 | Aeronautical mobile (R) |
| License Type | Aeronautical service (licensed, safety-of-life protected) |
| Primary Application | – |
| Primary Services | – |
| Spurious Emission [dBm] | -30 (baseline) |
| Lower Neighbor Use | Aeronautical radionavigation (VOR/ILS) |
| Upper Neighbor Use | Meteorological-satellite / Space operation |
| Licensing Model | Licensed (Aviation) |
| Typical Services Devices | Air traffic comms |
| US FCC Alloc | Aeronautical Mobile (R) Airband (8.33/25 kHz)– |
| CA IC Alloc | Aeronautical Mobile (R) Airband– |
| UK Ofcom Alloc | Aeronautical Mobile (R) Airband– |
| US Ref | 47 CFR Part 87 (Aviation) |
| Typical Bandwidths | 6–8 kHz |
| Market Licensing Model | Licensed (Aviation) |
| Market Common Devices | Aircraft radios, ATC comms |
| Fresnel Radius (1st, 1 km) [m] | 23.482722058869 |
| Typical Bandwidths (Estimated) | 6–8 kHz |
| Auction Status | – |
| Refarming Use | No |
| Typical Site Spacing km | – / – |
| Device Ecosystem Size | Medium |
| Traffic Load Share | Coverage-heavy, low capacity share |
| Device Hotspots (MHz) | 136 |
| Device Category | Specialized Industrial / Scientific Equipment |
| Typical Use Cases | – |
| Typical Center Frequencies [MHz] | – |
| Rule Part (Fcc Or Region) | – |
| Modulation (Device) | Varies by device |
| Channel Width (Device) [kHz] | Varies |
| Device Region Profiles | Varies by country / allocation |
| Per-Region EIRP Or Duty (Device) | Varies by regulation |
| Allocation Relevance (Device) | Medium |
| Adjacent-Band Collision Risks (Device) | Low–Moderate |
| Example Devices Or Skus | Specialized Industrial / Scientific Equipment |
| Antenna Form Factor (Typical) | ¼-wave ≈ 55.1 cm |
| Power Source Or Duty Profile (Typical) | – |
🛡️ Regulatory & Neighbors
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Lower Band Frequency Limit | 118 |
| Upper Band Frequency Limit | 137 |
| Rx Blocking Min dBm | -15 (planning) |
| Lower Neighbor Use | Aeronautical radionavigation (VOR/ILS) |
| Upper Neighbor Use | Meteorological-satellite / Space operation |
| Lower Neighbor Band | Aeronautical radionavigation (VOR/ILS) |
| Lower Neighbor Range | 108.000–118.000 MHz |
| Upper Neighbor Label | Meteorological-satellite / Space operation |
| Upper Neighbor Range | 137.000–143.000 MHz |
| Adjacent-Band Collision Risks (Device) | Low–Moderate |
| Real-World Range (Indoor/Outdoor) | – |
| US FCC Alloc | Aeronautical Mobile (R) Airband (8.33/25 kHz)Aeronautical Mobile (R) Airband (8.33/25 kHz) |
| CA IC Alloc | Aeronautical Mobile (R) AirbandAeronautical Mobile (R) Airband |
| UK Ofcom Alloc | Aeronautical Mobile (R) AirbandAeronautical Mobile (R) Airband |
| Regulatory References | US: 47 CFR Part 87 (Aviation); CA: ISED Aeronautical (per Radiocommunication Regs); UK: UK FAT (Aeronautical) |
| Global Harmonization | Regional |
| Crossborder Coordination | High |
| Sharing Mechanism | – |
| Auction Status | – |
| Guard Or Pair | – |
📈 Market & Measurements
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Noise Floor | -105 dBm (est.) |
| Interference Cases | – |
| Lower Neighbor Range | 108.000–118.000 MHz |
| Upper Neighbor Range | 137.000–143.000 MHz |
| Interference Notes | Critical safety communications |
| Market Licensing Model | Licensed (Aviation) |
| Market Commercial Value | High (safety-of-life) |
| Market Common Devices | Aircraft radios, ATC comms |
| Market Deployment Density | High at airports, sparse elsewhere |
| Noise Floor (Estimated) | -105 dBm (est.) |
| Market Commercial Value (Estimated) | High (safety-of-life) |
| Ecosystem Maturity | Emerging |
| Indoor Penetration | Good |
| Known Interference | Airband safety-of-life – interference strictly controlled |
| Device Ecosystem Size | Medium |
| Real-World Range (Indoor/Outdoor) | – |
| Antenna Form Factor (Typical) | ¼-wave ≈ 55.1 cm |
| Ecosystem Maturity | Emerging |
| Device Ecosystem Size | Medium |
| Chipset Availability | Limited / TBD |
| Operator Deployments | Limited operators |
| Technology Generations Deployed | Multiple / TBD |
| Roaming Support | – |
| Traffic Load Share | Coverage-heavy, low capacity share |
| Indoor Penetration | Good |
| Known Interference | Airband safety-of-life – interference strictly controlled |
| Occupancy | Medium |
| Occupancy Bucket Pct | 10–30% |
| Latency Profile | – |
| Common Channels Or Profiles | – |
| Security Features | – |
| Lbt Or Fhss Requirement | – |
| Popularity (Installed Base) | – |
| Coexistence Tips | – |
| Latency Class | – |
| Device Hotspots (Scoped && Tagged) | – |